The post describes a MATLAB script for obtaining ABAQUS tetrahedral volume mesh from surface mesh of grain boundaries generated in Dream.3D.
Intro
In the previous post, I described a MATLAB script to write hexahedral ABAQUS mesh for a microstructure generated in Dream.3D. Brick elements make for a good mesh quality and thus a decent numerical stability of finite element simulations. At the same time, the use of brick elements inevitably leads to ladder-shaped grain boundaries.
Sometimes, it is desired to include the effect of the intricate curvature of grain boundaries in finite element simulations. For example, with realistic grain boundaries incorporated in the finite element models, it is possible to track the evolution of grain boundary facet normals or even grain boundary character disribution during plastic deformation (see Knezevic et al., 2014).
Dream.3D currently allows for meshing grain boundaries by triangular elements (see Lee et al., 2014 for details). It is often a challenge to produce volume mesh from surface mesh of grain boundaries, which may require commercial software.
This post describes an alternative method based on an open-source MATLAB toolbox for grain boundary-conformed mesh generation. The described method requires running a single MATLAB script that writes mesh into a text file that can be readily imported in ABAQUS.
The script
The MATLAB script presented here does the following:
- Reads nodes, triangles of surface mesh and feature centroids generated in Dream.3D (ver. 4.2.x)
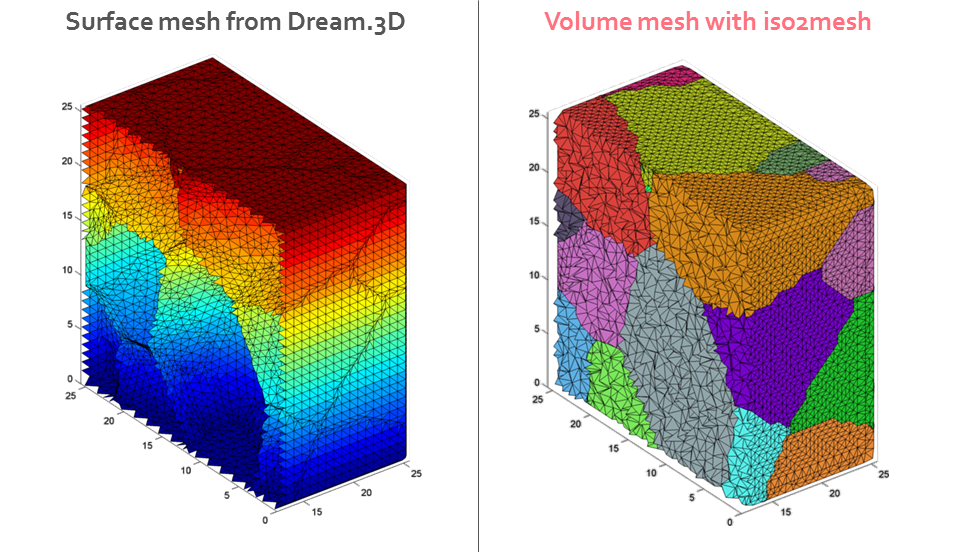
- Generates volume tetrahedral mesh using iso2mesh toolbox
- Writes the generated mesh into a file in ABAQUS input file format
Usage
To use the script, do the following:
- Download iso2mesh toolbox and add it to MATLAB path
- Download
dream2abatet.mscript and put it to a MATLAB folder - Run Dream.3D pipeline to write nodes, triangles, features files
- Run
dream2abatet.mscript pointing to the three Dream.3D files
Example
My repository for dream2abatet script contains a set of example files for testing and getting familiar with the framework. The files that can be used for a test run of the script are
- ex_nodes.in
- ex_tri.in
- ex_features.in
You can use them to generate your first mesh as follows
- Download the repo, extract the files to a MATLAB folder.
- Run
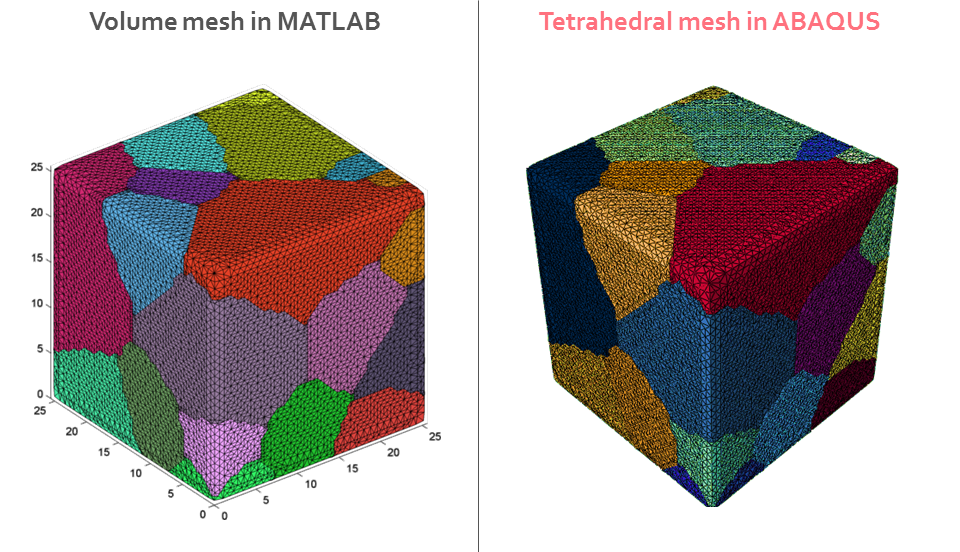
dream2abatet('ex_nodes.in','ex_tri.in','ex_features.csv',0.75,0.5,true)in MATLAB and you should get a file dream.inp containing your mesh. Check it in ABAQUS/CAE by setting colors in the Viewer according to Sets. The result should look like the image above.
The repository also contains an example Dream.3D (ver. 4.2.5) pipeline - ex_pipe.txt, which writes the ex_nodes.in, ex_tri.in, ex_features.csv files for a 32x32x32 single-phase microstructure grid.
Tip: Both Dream.3D and iso2mesh allow for smoothing of the surface mesh. Furthermore, the function of iso2mesh toolbox responsible for the mesh generation takes several parameters as input, such as keepRatio and maxVolElement – the number of surface elements to be preserved during volume mesh generation and the maximum volume of the tetrahedral element (set as 0.75 and 0.5 in the example above). You can go through the documentation of both software packages to get familiar with the meshing and smoothing parameters as well as to experiment with them until a satisfactory mesh quality is achieved.
Known limitations
- The script requires grain centroids. The only option to export centroids in Dream.3D ver. 4.2.x seems to be Write Goal Attributes in Pack Primary Phases filter. Since the generated microstructure does not necessarily match the goal attributes exactly, some grains may be missing in ABAQUS sets.
- The workflow does not work well with periodic boundaries set in Dream.3D: either generation of volume mesh will fail or the number of missing grains in ABAQUS sets will increase.
- Generation of volume mesh may fail for some microstructures (Invalid PLC error). In such cases, rerun Dream.3D pipeline and try again or try different Dream.3D settings.
- No information on phases will be passed to ABAQUS in the current version of the script.